
Is a digital ledger system that enables secure, decentralized, and transparent record-keeping of
transactions across a network of computers. Instead of a traditional centralized database, where a single entity controls the data, blockchain distributes data and transactions across nodes, which are multiple computers, connected on a peer-to-peer network. Key features of blockchain technology include:

There is no central authority governing the blockchain network. Instead, all participating nodes maintain a copy of the entire blockchain, ensuring that there is no single point of failure or control.

Blockchain uses advanced cryptographic techniques to secure data and transactions on the network. Each block is cryptographically linked to the previous block, making it impossible to alter the contents of a block without being detected.

Every transaction on the blockchain is recorded in a block, which is linked to the previous block, forming a chain of blocks. These blocks are absolutely immutable, which means that once a block is added to the chain, it cannot be altered or deleted. This creates a transparent and auditable record of transactions.

To validate and add new transactions to the blockchain, participants must agree on the validity of the transactions through a consensus mechanism. Popular consensus mechanisms include Proof of Work (PoW) and Proof of Stake (PoS).

Blockchain addresses the risk of tampering through proof of work—a piece of data that is computationally difficult to produce but easy to validate. Proof of work replaces the trust of a central authority with trust by computation.

Smart contracts are self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement directly written into code on the blockchain. They automatically enforce the terms of the contract when predefined conditions are met, eliminating the need for intermediaries.

Public blockchains, such as bitcoin are accessible to any and all users whereas private blockchains restrict access to a few approved users. The computational overhead is lower in the case of private blockchains as they do not require proof of work for participation, compared to public blockchains and are suitable for internal use by organizations.

Financial services struggle with archaic operational processes, slow payment settlements, limited transparency, and security vulnerabilities. Blockchain enhances the efficient digitization of financial instruments, which increases liquidity, lowers cost of capital, and reduces counterparty risk. Settlements can be made faster and cheaper using blockchain technology, since a need to centrally verify the transactions is circumvented. Blockchain also simplifies logistically complicated cross-border transactions involving different types of financial assets.


The entertainment industry suffers an estimated loss of $71 billion annually, owing to piracy, fraud, and intellectual property theft of digital items. Blockchain could track the life cycle of any content, which has the potential not only to protect digital content, but also to facilitate the distribution of authentic digital collectibles.

Existing global supply chains are poorly tracked, inefficient, and as a result, quite often exploitative. Blockchain can facilitate accurate asset tracking, enhanced licensing of services, software, and products, and build transparency into the provenance of consumer goods until the point of consumption.

Enables the digitization of financial instruments and assets. This enhances democratized access to real estate investment opportunities, wider access to global markets, fractionalization of ownership, and increased liquidity.

Procedural delays caused by conventional methods of establishing the authenticity of information across government agencies can be avoided by enabling digital citizen record keeping over a blockchain network. The technology helps not only to speed up public service delivery but also to make it more transparent.

Industries such as the fashion and luxury industry rapidly changes with the demands of consumers. Their premium products could be tracked from their point of origin using digital tokens which protect them from threats of counterfeits through the supply chain. By enhancing supply chain operations and improving data management tools, the risk of grey markets can be nullified. Apart from these, multi-brand loyalty programs can be made easily redeemable based on blockchain technologies.
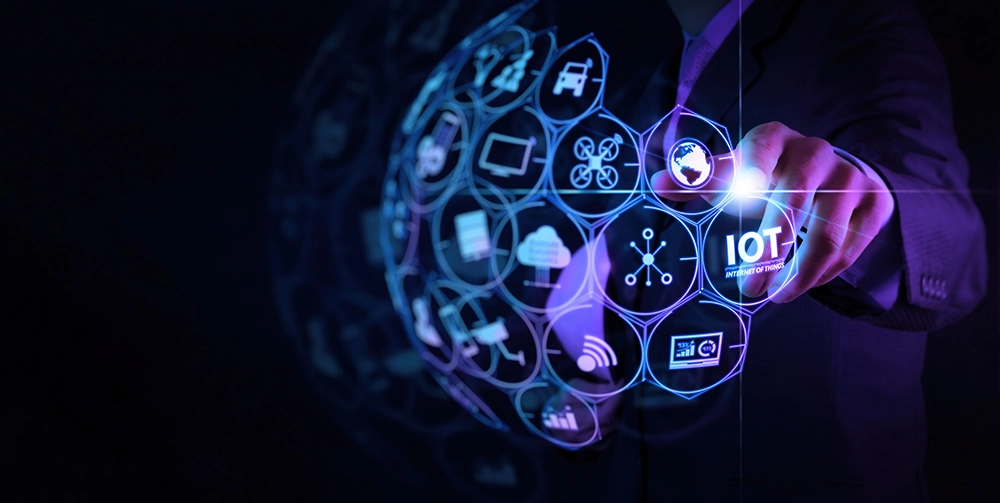

The centralized architecture of the current crop of IoT platforms is being reinvented with the help of blockchain technology to facilitate decentralized and autonomous interaction between devices, towards building a more cost-efficient and trusted IoT.
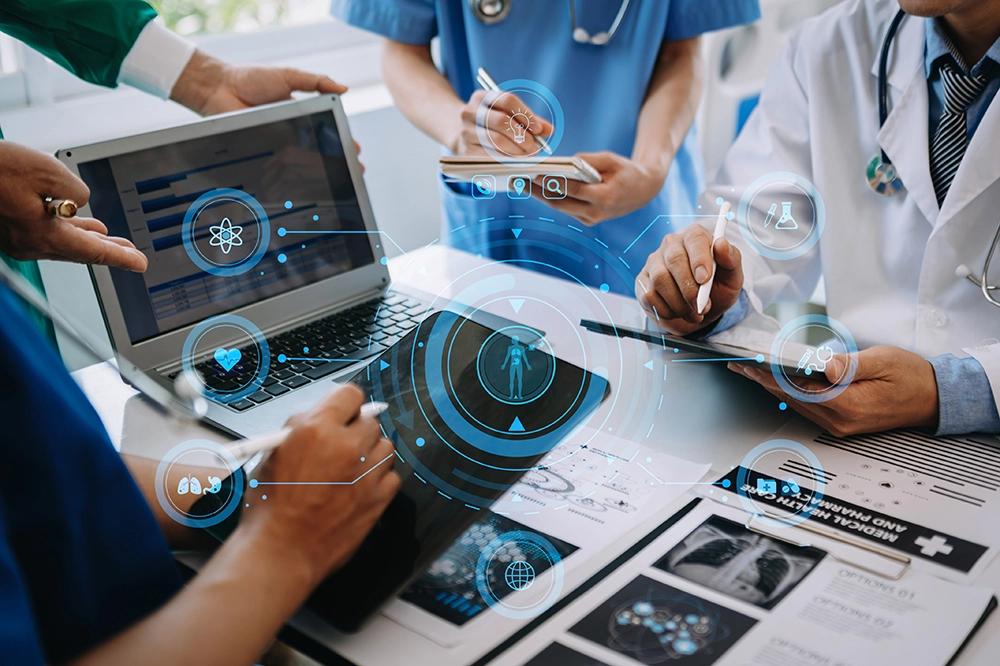

Blockchain-based healthcare solutions will enable more efficient, secure and faster medical data management as well as medical supply tracking. This could exponentially improve patient care, ensure the authenticity of drugs circulating global markets as well as facilitate the advancement of medical discoveries. Interoperable access to health data would lead to better diagnosis and decisions, and this can be facilitated by a shared data infrastructure.
Trading consortiums and companies are recognizing the transformative impact of blockchain in operating global supply chains, managing trade and finance, as well as unlocking new business models. Blockchain products could offer secure digitization, which enables tokenization of existing letters of credit, documents, and more.

Blockchain offers a secure and decentralized way to track and manage the flow of goods and information across the supply chain network. A blockchain-based system improves transparency, traceability, and efficiency in the supply chain process. Implementation of blockchain technology in supply chain management would streamline operations, enhance visibility and transparency, as well as strengthens trust among stakeholders, ultimately leading to a more efficient and secure supply chain ecosystem.
Following are the actors:

All parties have access to real-time, transparent information about the supply chain, fostering trust and accountability.
The immutability of blockchain ensures a secure and auditable record of every transaction and asset movement.
Automation through smart contracts reduces manual processes and speeds up transactions between parties.
Verification of product provenance and quality leads to improved product safety and consumer confidence.
The decentralized nature of blockchain reduces the risk of fraud, counterfeiting, and data manipulation along the supply chain.